Introduction
Being able to configure the way a protocol plugin will manage the communication with the remote servers or clients using the protocol stack parameters, whether communication is secured or not, how the messages attributes are translated from the input protocol data model to the output protocol data model and what kind of rules (filters, math, routing, etc..) to apply to the messages that are exchanges with the remote systems are key features of any protocol translation gateway.
In this design document we will be describing the implementation of the 3 main plugins configuration data models: protocol stack configuration (including application layer, transport layer and security layer), protocols translation configuration, exchanged datapoints configuration and data processing/filtering rules.
FledgePOWER being built on top of Fledge, all the configuration will be described using JSON data structures using nested objects and will be sent to the gateway using the provided HTTP API.
Overview
Functional architecture
Configuration data categories
Protocol translation
Pivot format definition
Before diving into the details of the specification, it is useful to illustrate some use cases. They should help demonstrate how the specification is expected to be used and to help understand the benefits of a pivot format.
The objective of a gateway is to allow communication between different systems by providing some translation mechanisms from one means of communication to another one.
All translation mechanisms introduce a limitation of functionality in the translated space compared to the original space. The major challenge is to provide some correspondences between the two systems, with a limited impact to the original scope of features.
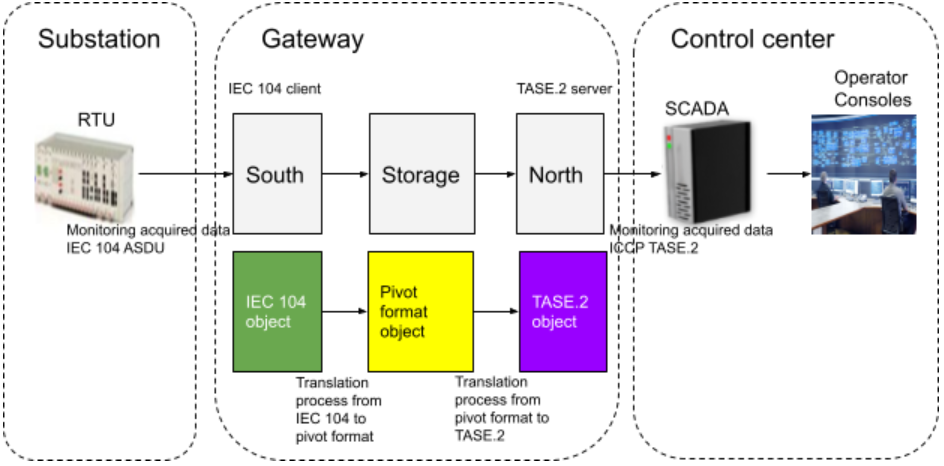
Use case 1: monitoring
In this use case, monitoring data are acquired from a field device called RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) which acts as a IEC 104 server (slave) and are exposed to the central SCADA which acts as a ICCP TASE.2 client. Each incoming message from the RTU comes as an IEC 104 ASDU object. The south service plugin applies a first translation process which consists of (1) reading and checking the ASDU object using the IEC 104 data model and (2) mapping each data attribute to the corresponding pivot format data attribute. Once the message is converted to a pivot format object, it can then be stored or consumed by the north or any other service. The north service plugin can then apply a second translation process which consists of (3) reading and checking the pivot format object using the pivot format data model and (4) mapping each data attribute to the corresponding TASE.2 data attribute. The resulting TASE.2 object can then be exposed to the TASE.2 client by the north service plugin.
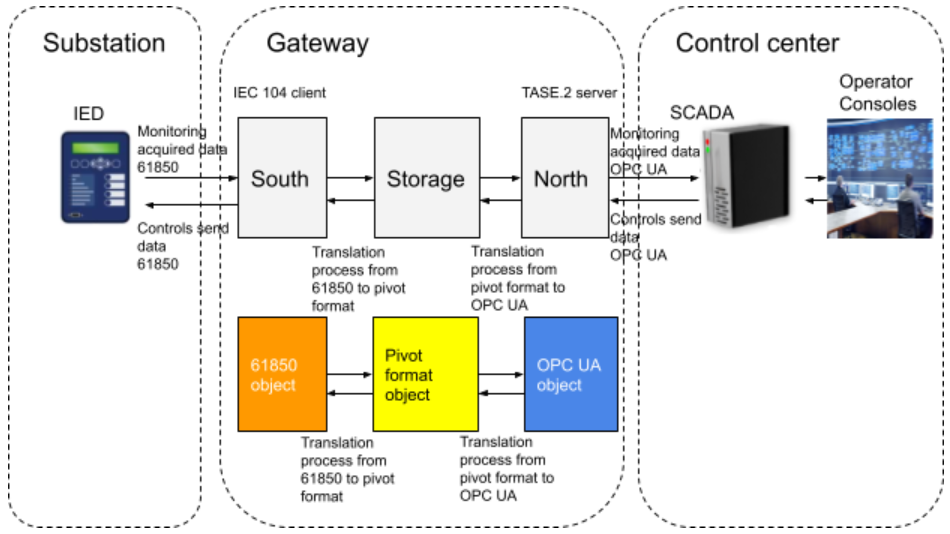
Use case 2: monitoring and control
In this use case data flows in two directions: monitoring and control.
Monitoring data are acquired from a field device called IED (Intelligent Electronic Device) which acts as a 61850 MMS server and are exposed to the central SCADA which acts as a OPC UA client. Each incoming message from the IED comes as a 61850 MMS object. The south service plugin applies a first translation process which consists of (1) reading and checking the 61850 MMS object using the 61850 MMS data model and (2) mapping each data attribute to the corresponding pivot format data attribute. Once the message is converted to a pivot format object, it can then be stored or consumed by the north or any other service. The north service plugin can then apply a second translation process which consists of (3) reading and checking the pivot format object using the pivot format data model and (4) mapping each data attribute to the corresponding OPC UA data attribute. The resulting OPC UA object can then be exposed to the OPC UA client by the north service plugin.
Control data are received from the control center SCADA which acts as a OPC UA client and are sent to the IED which acts as a 61850 server. Each incoming message from the control center SCADA comes as an OPC UA object. The north service plugin applies a first translation process which consists of (1) reading and checking the OPC UA object using the OPC UA data model and (2) mapping each data attribute to the corresponding pivot format data attribute. Once the message is converted to a pivot format object, it can then be stored or consumed by the south or any other service. The south service plugin can then apply a second translation process which consists of (3) reading and checking the pivot format object using the pivot format data model and (4) mapping each data attribute to the corresponding 61850 MMS data attribute. The resulting 61850 MMS object can then be exposed to the 61850 client by the south service plugin.
Benefits and challenges of a pivot format
Benefits
The main benefit of the pivot format is it allows decoupling the protocols data model from each other. Each south or north plugin deals with the complexity and the specifics of a given protocol without interfering with the core of the gateway or with another south/north plugin. Adding new protocol plugins or maintaining existing ones is then made much easier. This contributes in maintaining the whole gateway system at a low level of complexity thus minimizing the costs of new developments or maintenance.
Challenges
In order to reach the goal of simplicity we want to achieve, the main challenge is to be able to build a pivot format that is technically independent from the protocols. The data model should also be neutral regarding protocols data models.
Pivot format design proposition
{
"data_object_header":{
"doh_type":"some_value",
"doh_name":"some_value",
"doh_ca":"some_value",
"doh_oa":"some_value",
"doh_cot":"some_value",
"doh_test":"some_value",
"doh_negative":"some_value",
"doh_version":"some_value",
"doh_src_prot":"some_value"
},
"data_object_item":{
"doi_ioa":"some_value",
"doi_value":"some_value",
"doi_qual_class":"some_value",
"doi_quality":"some_value",
"doi_current_src":"some_value",
"doi_normal_src":"some_value",
"doi_normal_value":"some_value",
"doi_ts_class":"some_value",
"doi_ts":"some_value",
"doi_ts_qual":"some_value",
"doi_ts_sum_time":"some_value",
"doi_ts_subs":"some_value",
"doi_cov_class":"some_value",
"doi_cov_counter":"some_value"
}
}
The pivot format uses JSON with a header and item structure.
The header object holds the common attributes of a telecontrol message.
Each item object holds the specific attributes of an information point whether it is a measurement, a state, a command, etc...
IEC 104 south plugin (client/master)
IEC 104 Protocol stack configuration
The IEC 104 protocol stack configuration specifies communication parameters and is a collection of entries containing information about OSI Transport and OSI Application layers objects.
Each entry is comprised of attributes that describe the object. All the configuration data are structured using JSON.
Each entry shall be mapped with the corresponding configuration function in the chosen implementation protocol library.
Attributes definition
| Attribute | Description | Expected values | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | this identifies the protocol stack | iec104client, iec104server, tase2client, tase2server, 61850client, 61850server, etc... | Yes |
| version | version number of the configuration file | 2 digits x.y => x = major change, y = minor change | Yes |
| connection.path | array of connection paths | ||
| connection.path.srv_ip | IP address to remote IEC 104 server | IP address | Yes |
| connection.path.clt_ip | client IP in case of multiple network interfaces server access | IP address | No |
| connection.path.port | port number to remote IEC 104 server | default = 2404 | No |
| tls | activation of TLS (see tls configuration chapter for details) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| k_value | Maximum number of outstanding (unacknowledged) APDU's at a given time | default = 12 | No |
| w_value | Acknowledge the reception latest after this number of APDU's | default = 8 | No |
| t0_timeout | time out of connection establishment | default = 10 | No |
| t1_timeout | time out for send or test APDU's | default = 15 | No |
| t2_timeout | time out for acknowledges in case of no data messages (t2 < t1) | default = 10 | No |
| t3_timeout | time out for sending test frames | default = 20 | No |
| conn_all | establish all paths within one connection at the same time (=TRUE) or only one (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| start_all | start communication on all established paths at the same time (=TRUE) or on only one (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| conn_passv | establish connection even in passive mode (=TRUE) or not (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| orig_size | size of "Originator Address" | 0, 1 (byte) | No |
| orig_addr | Originator Address | default = 0 | No |
| ca_asdu_size | size of "Common Address of ASDU" | default = 2 (byte) | No |
| ioaddr_size | size of 'Information Object Address' | default = 3 (byte) | No |
| startup_time | time to wait for startup completion | default = 180 (seconds) | No |
| asdu_size | maximum ASDU size in transmission direction, if set to "0" => maximum possible value is automatically used. | default = 0 (byte) | No |
| gi_time | time to wait for General Interrogation (GI) completion | default = 0 (seconds) | No |
| gi_cycle | send General Interrogation (GI) cyclically | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| gi_all_ca | send a separate GI request to every CA; otherwise a broadcast GI request is used | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| gi_repeat_count | repeat GI for this number of times in case it is incomplete | default = 2 | No |
| disc_qual | information object quality in case of interrupted connection | IV = Invalid, NT = Not Topical, default = NT | No |
| send_iv_time | time delay before infos are sent as invalid (0 = deactivated) | default = 0 | No |
| tsiv | specifies what to do with a time stamp marked as 'invalid' | remove, process, default = remove | No |
| utc_time | UTC timezone (=TRUE) or local timezone (=FALSE) for time conversion | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| comm_wttag | use commands with time tag (=TRUE) or without time tag (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| comm_parallel | maximum number of commands to be executed at in parallel (0 = unlimited) | default = 0 | No |
| exec_cycl_test | execute cyclical test requests (C_TS_NA_1/C_TS_TA_1) in monitoring direction (=TRUE) or not (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| startup_state | startup in active mode (=TRUE) or in passive mode (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
| reverse | allow transmission of information objects in reverse direction (=TRUE) or only in standard direction (=FALSE) | TRUE, FALSE, default = FALSE | No |
Configuration JSON file structure
{
"protocol_stack":{
"name":"iec104client",
"version":"1.0",
"transport_layer":{
"connection":{
"path":[
{
"srv_ip":"192.168.0.10",
"clt_ip":"",
"port":2404
},
{
"srv_ip":"192.168.0.11",
"clt_ip":"",
"port":2404
}
],
"tls":"NONE"
},
"k_value":12,
"w_value":8,
"t0_timeout":10,
"t1_timeout":15,
"t2_timeout":10,
"t3_timeout":20,
"conn_all":true,
"start_all":false,
"conn_passv":false
},
"application_layer":{
"orig_size":1,
"orig_addr":"",
"ca_asdu_size":2,
"ioaddr_size":3,
"startup_time":180,
"asdu_size":0,
"gi_time":60,
"gi_cycle":0,
"gi_all_ca":false,
"gi_repeat_count":2,
"disc_qual":"NT",
"send_iv_time":0,
"tsiv":"REMOVE",
"utc_time":"false",
"comm_wttag":false,
"comm_parallel":0,
"exec_cycl_test":false,
"startup_state":"active",
"reverse":false"
}
}
}
Path exploration
In redundant network configuration or generally in cases where several communication paths exist between one client and one server, the path checking exploration mechanism allows the client to try all the paths one by one without making any difference between them. The client uses the first available path. On disconnection this procedure starts again from the beginning.
TLS configuration
The CS 104 standard can also be used with TLS to realize secure and authenticated connections.
3 parameters are needed to set up the TLS secured connection:
- private key file
- server certificate
- root certificate (CA)
Fledge's certificate store allows certificates to be stored and used by the south plugins.
{
"tls_conf:": {
"private_key": "server-key.pem",
"server_cert": "server.cer",
"ca_cert": "root.cer"
}
}
IEC 104 exchanged ASDU configuration
In this chapter we will describe the configuration of the exchanged ASDU. This configuration allow to specify a list of supported ASDU types and a list of ASDU objects. The protocol plugin is expected to make some controls against each entry of the configuration to check:
- if CA of ASDU is known otherwise throw an error message.
- if IOA is known otherwise throw an error message.
- if type of ASDU is known otherwise an error message.
- The label attribute shall be used to populate the Fledge's DataPoint Asset Name attribute.
Configuration JSON file structure
{
"exchanged_data_layer":{
"name":"iec104client",
"version":"1.0",
"asdu_list":[
{
"ca":"41025",
"type_id":"M_ME_NA_1",
"label":"TM-1",
"ioa":"4202832"
},
{
"ca":"41025",
"type_id":"M_ME_NA_1",
"label":"TM-2",
"ioa":"4202852"
},
{
"ca":"41025",
"type_id":"M_SP_TB_1",
"label":"TS-1",
"ioa":"4206948"
}
]
}
}
IEC 104 to pivot format translation
IEC 104 ASDU data model
Reference: NF EN 60870-5-101 § 7.3.1.22
TYPE IDENT 30: M_SP_TB_1
DATA UNIT IDENTIFIER
TYPE IDENTIFICATION
VARIABLE STRUCTURE QUALIFIER
CAUSE OF TRANSMISSION
COMMON ADDRESS OF ASDU
INFORMATION OBJECT 1
INFORMATION OBJECT ADDRESS
SIQ
CP56Time2a
INFORMATION OBJECT i
INFORMATION OBJECT ADDRESS
SIQ
CP56Time2a
IEC 104 to pivot format conversion configuration model
{
"protocol_translation_layer":{
"name":"iec104_to_pivot",
"version":"1.0",
"mapping":{
"data_object_header":{
"doh_type":"type_id",
"doh_ca":"ca",
"doh_oa":"oa",
"doh_cot":"cot",
"doh_test":"istest",
"doh_negative":"isnegative"
},
"data_object_item":{
"doi_ioa":"ioa",
"doi_value":"value",
"doi_quality":"quality_desc",
"doi_ts":"time_marker",
"doi_ts_flag1":"isinvalid",
"doi_ts_flag2":"isSummerTime",
"doi_ts_flag3":"isSubstituted"
}
}
}
}
Conversion process
NB: The conversion process shall produce as many pivot format objects as information objects in the source ASDU.
Pivot format resulting object
{
"data_object_header":{
"doh_type":"some_value",
"doh_name":"not_populated",
"doh_ca":"some_value",
"doh_oa":"some_value",
"doh_cot":"some_value",
"doh_test":"some_value",
"doh_negative":"some_value",
"doh_version":"some_value",
"doh_src_prot":"some_value"
},
"data_object_item":{
"doi_ioa":"some_value",
"doi_value":"some_value",
"doi_qual_class":"not_populated",
"doi_quality":"some_value",
"doi_current_src":"not_populated",
"doi_normal_src":"not_populated",
"doi_normal_value":"not_populated",
"doi_ts_class":"not_populated",
"doi_ts":"some_value",
"doi_ts_qual":"some_value",
"doi_ts_sum_time":"some_value",
"doi_ts_subs":"some_value",
"doi_cov_class":"not_populated",
"doi_cov_counter":"not_populated"
}
}
IEC 104 north plugin (server/slave)
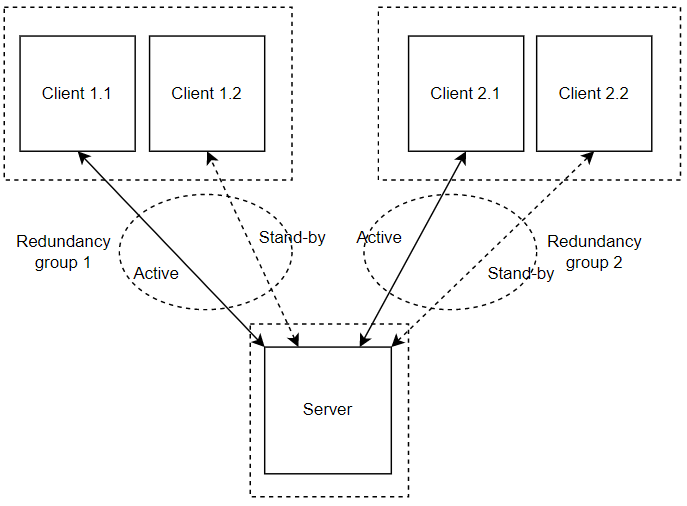
IEC 104 redundancy server modes
Multiple redundancy groups
The MZ Automation lib60870 server provides 3 different modes regarding the support of redundant connections and events queue handling:
- The default mode (CS104_MODE_SINGLE_REDUNDANCY_GROUP) allows only a single active client connection.
- The second mode (CS104_MODE_CONNECTION_IS_REDUNDANCY_GROUP) allows multiple active client connections.
- The third mode (CS104_MODE_MULTIPLE_REDUNDANCY_GROUPS) allows multiple active client connections while preserving events when no client is connected.
In the case of this design, the south plugin will be implemented with CS104_MODE_MULTIPLE_REDUNDANCY_GROUPS server mode.
This mode allows multiple active client connections while preserving events when no client is connected. In this mode clients can be assigned to specific redundancy groups. The assignment is based on the IP address of the client. A redundancy group can have multiple simultaneous connections but only one of these connections can be active. The number of activated connections is restricted by the number of redundancy groups. Each redundancy group has a dedicated event queue.
It can be set with the CS104_Slave_setServerMode function:
CS104_Slave_setServerMode(slave, CS104_MODE_MULTIPLE_REDUNDANCY_GROUPS);
Multiple redundancy groups example
IEC 104 Protocol stack configuration
Configuration JSON file structure
{
"protocol_stack": {
"name": "iec104server",
"version": "1.0",
"transport_layer": {
"bind_on_ip": "FALSE",
"port": 2404,
"tsecurity": "NONE",
"k_value": 12,
"w_value": 8,
"t1_timeout": 15,
"t2_timeout": 10,
"t3_timeout": 20,
"open_new_path": "TRUE",
"bind_on_active": "FALSE",
"disc_on_iframe": "TRUE"
},
"application_layer": {
"orig_size": 1,
"orig_addr": "0",
"ca_asdu_size": 2,
"ioaddr_size": 3,
"struct_addr": "FALSE",
"asdu_size": 0,
"default_class": "CLASS1",
"time_sync": "FALSE",
"comm_exec_timeout": 20000,
"comm_recv_timeout": 5000,
"auto_comm_actcon": "FALSE",
"auto_comm_actterm": "TRUE",
"cmd_block_sel": "FALSE",
"abs_time": "TRUE",
"tzsource": "OS",
"set_wday": "TRUE",
"tsiv": "IGNORE",
"spon_in_passive": "TRUE",
"reset": "TRUE",
"filter_orig": "FALSE",
"lifeact": "TRUE",
"startup": "FALSE",
"active": "TRUE"
}
}
}
Pivot format to IEC 104 translation
Pivot format to IEC 104 conversion configuration model
{
"protocol_translation_layer":{
"name":"pivot_to_iec104",
"version":"1.0",
"mapping":{
"data_object_header":{
"type_id":"doh_type",
"ca":"doh_ca",
"oa":"doh_oa",
"cot":"doh_cot",
"istest":"doh_test",
"isnegative":"doh_negative"
},
"data_object_item":{
"ioa":"doi_ioa",
"value":"doi_value",
"quality_desc":"doi_quality",
"time_marker":"doi_ts",
"isinvalid":"doi_ts_qual",
"isSummerTime":"doi_ts_sum_time",
"isSubstituted":"doi_ts_subs"
}
}
}
}
Conversion process
IEC 104 ASDU resulting object
DATA UNIT IDENTIFIER
TYPE IDENTIFICATION
VARIABLE STRUCTURE QUALIFIER
CAUSE OF TRANSMISSION
COMMON ADDRESS OF ASDU
INFORMATION OBJECT 1
INFORMATION OBJECT ADDRESS
SIQ
CP56Time2a
ICCP TASE.2 north plugin (server)
ICCP TASE.2 Protocol stack configuration
<not yet designed>
ICCP TASE.2 exchanged data points configuration
<not yet designed>
ICCP TASE.2 to pivot format translation
DataValue Indication Point data model
PointName
PointType
PointRealValue
PointStateValue
PointDiscreteValue
QualityClass
Validity
CurrentSource
NormalSource
NormalValue
TimeStampClass
TimeStamp
TimeStamp Quality
COVClass
COVCounter
ICCP TASE.2 to pivot format conversion configuration model
{
"protocol_translation_layer":{
"name":"tase2_to_pivot",
"version":"1.0",
"mapping":{
"data_object_header":{
"doh_type":"PointType",
"doh_name":"PointName"
},
"data_object_item":{
"doi_value":"PointRealValue", //PointStateValue or PointDiscreteValue
"doi_qual_class":"QualityClass",
"doi_quality":"Validity",
"doi_current_src":"CurrentSource",
"doi_normal_src":"NormalSource",
"doi_normal_value":"NormalValue",
"doi_ts_class":"TimeStampClass",
"doi_ts":"TimeStamp",
"doi_ts_qual":"TimeStamp Quality",
"doi_cov_class":"COVClass",
"doi_cov_counter":"COVCounter"
}
}
}
}
Conversion process
Pivot format resulting object
{
"data_object_header":{
"doh_type":"some_value",
"doh_name":"some_value",
"doh_ca":"not_populated",
"doh_oa":"not_populated",
"doh_cot":"not_populated",
"doh_test":"not_populated",
"doh_negative":"not_populated",
"doh_version":"some_value",
"doh_src_prot":"some_value"
},
"data_object_item":{
"doi_ioa":"not_populated",
"doi_value":"some_value",
"doi_qual_class":"some_value",
"doi_quality":"some_value",
"doi_current_src":"some_value",
"doi_normal_src":"some_value",
"doi_normal_value":"some_value",
"doi_ts_class":"some_value",
"doi_ts":"some_value",
"doi_ts_qual":"some_value",
"doi_ts_sum_time":"not_populated",
"doi_ts_subs":"not_populated",
"doi_cov_class":"some_value",
"doi_cov_counter":"some_value"
}
}
Pivot format to ICCP TASE.2 translation
Pivot format to ICCP TASE.2 conversion configuration model
{
"protocol_translation_layer":{
"name":"pivot_to_tase2",
"version":"1.0",
"mapping":{
"data_object_header":{
"PointType":"doh_type",
"PointName":"doh_name"
},
"data_object_item":{
"PointRealValue": "doi_value", //PointStateValue or PointDiscreteValue
"QualityClass":"doi_qual_class",
"Validity":"doi_quality",
"CurrentSource":"doi_current_src",
"NormalSource":"doi_normal_src",
"NormalValue":"doi_normal_value",
"TimeStampClass":"doi_ts_class",
"TimeStamp":"doi_ts",
"TimeStamp Quality":"doi_ts_qual",
"COVClass":"doi_cov_class",
"COVCounter":"doi_cov_counter"
}
}
}
}